Diabetes and Dementia
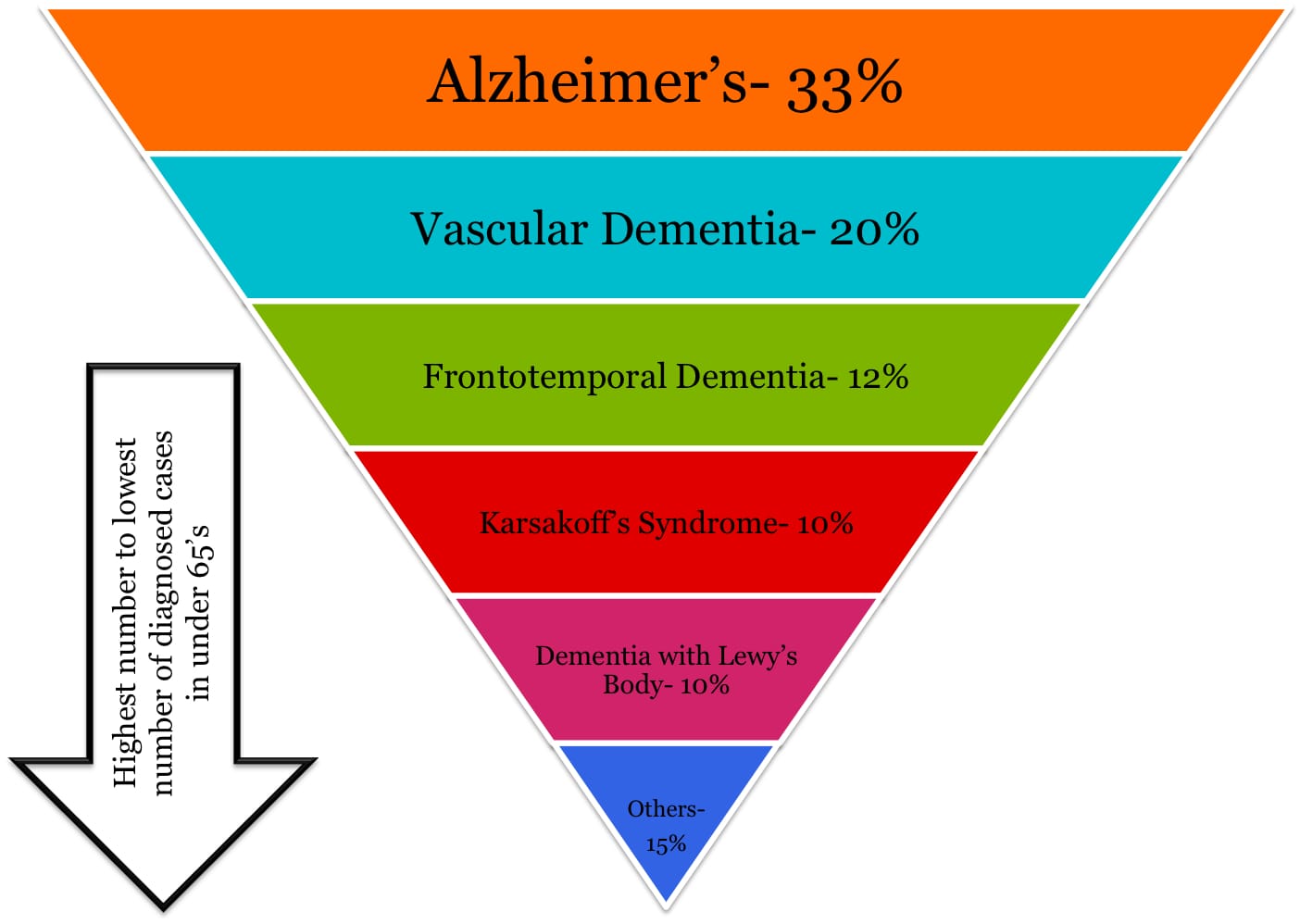
Dementia is majorly known as a cognitive disorder in which a person is mentally affected that is a person’s brain is affected. On a long term run he gradually loses his ability to think and remember, its affect is great enough to disturb a person's daily functioning. Other common symptoms include emotional problems, difficulties with language, and a decrease in motivation. Alzheimer's disease is the most common type of dementia constituting upto 50% - 70% of cases. Other common types include vascular dementia (25%), Lewy body dementia (15%), and frontotemporal dementia. Less common causes include normal pressure hydrocephalus, Parkinson's disease dementia, syphilis, and Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease among others. One person can have more than one type of dementia. Some researches states that Type 2 diabetes patients have a higher risk of getting affected with Alzheimer’s disease, the most common type of dementia on long term. Although no researches till now is able to prove how Alzheimer’s and diabetes are connected. Apart from that professional’s states they have proven cases of Diabetes raising the risk of cardiac diseases and stroke, which affects the heart and blood vessels. Damaged blood vessels in the central nervous system may contribute to Alzheimer’s disease. The brain depends on many different chemicals, which may be unbalanced by too much insulin. Some of these changes may help trigger Alzheimer’s disease. High blood sugar causes inflammation. This may damage brain cells and help Alzheimer’s to develop.
Recommended: - Diabetes conferences | Obesity conferences | Endocrinology conferences | Diabetes conferences 2023 | World congress on diabetes | Diabetes meetings | Endocrinology meetings | World diabetes congress |